Batam, strategically located near Singapore and Malaysia, is rapidly establishing itself as one of Indonesia’s foremost industrial and investment hubs. For businesses and investors aiming to penetrate Southeast Asian markets, a thorough understanding of Batam’s labor market, competitive wage structures, and regulatory environment is essential. This article explores the key elements that make Batam a compelling destination for business expansion.
A Dynamic Workforce Demographic
Batam’s workforce is youthful, skilled, and growing rapidly, with a labor force participation rate of 70%. Many workers are under 35, bringing energy and adaptability to industries like manufacturing and technology. The city’s industrial growth has developed a labor pool experienced in maintaining global standards, particularly in electronics, shipbuilding, and automotive sectors. This makes Batam an attractive hub for businesses looking to tap into Southeast Asia’s markets.
In addition to local talent, Batam attracts foreign professionals, particularly from Singapore, China, and Europe. These foreign workers bring specialized skills, contributing to high-tech and strategic industries. Their presence complements local talent, filling critical roles and enhancing Batam’s competitive edge in industries such as manufacturing and technology.
Key Industries Driving Employment
Manufacturing is the primary driver of Batam’s economy, employing the largest portion of the workforce. The electronics industry, in particular, has seen significant growth due to the city’s focus on technology-driven production. Other key sectors, like automotive and consumer goods manufacturing, also contribute to job creation and skill development for the local population.
While manufacturing remains dominant, Batam’s economy is diversifying into services, trade, and tourism. The growing hospitality and tourism sectors, fueled by visitors from neighboring countries, are creating new employment opportunities and expanding the city’s economic potential beyond its industrial roots. This diversification opens up new avenues for investors and businesses seeking to tap into Batam’s evolving landscape.
Competitive Wage Structure
One of the key advantages of operating in Batam is its competitive labor cost. In 2024, the minimum wage in Batam was set at Rp 4,685,050 per month for a 40-hour workweek. This wage level strikes a balance between ensuring worker welfare and maintaining business competitiveness, allowing companies to access a productive labor force without the high operational costs often associated with major cities like Jakarta or Surabaya.
The minimum wage policy in Batam is shaped by various economic factors, including inflation, economic growth, and the cost of living. In 2024, the determination of the minimum wage has garnered attention as the government collaborates with labor unions to establish a fair wage that supports both employee welfare and the economic viability of businesses. This cooperative approach aims to foster a stable labor market while encouraging investment in the region.
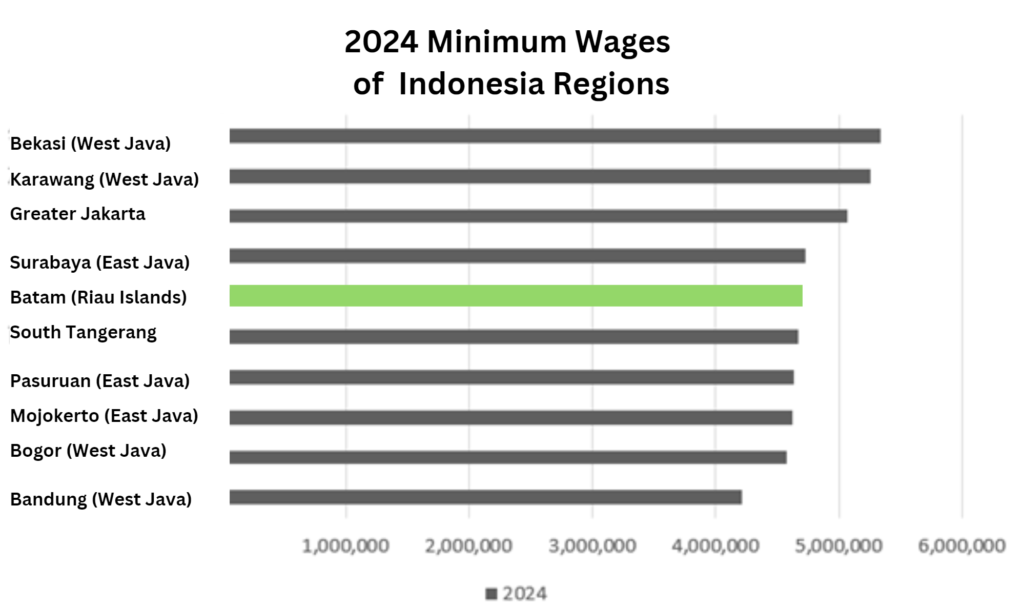
When compared to other regions in Indonesia, Batam’s minimum wage positions it in the middle tier. For example, while DKI Jakarta’s minimum wage is higher at Rp 5,067,381 per month, regions like Bekasi City and Karawang lead the country with minimum wages reaching Rp 5,343,430. This ranking illustrates that while Batam offers competitive wages, it remains manageable for businesses, ensuring that the region continues to attract investment.
Workforce Regulations and Labor Protections
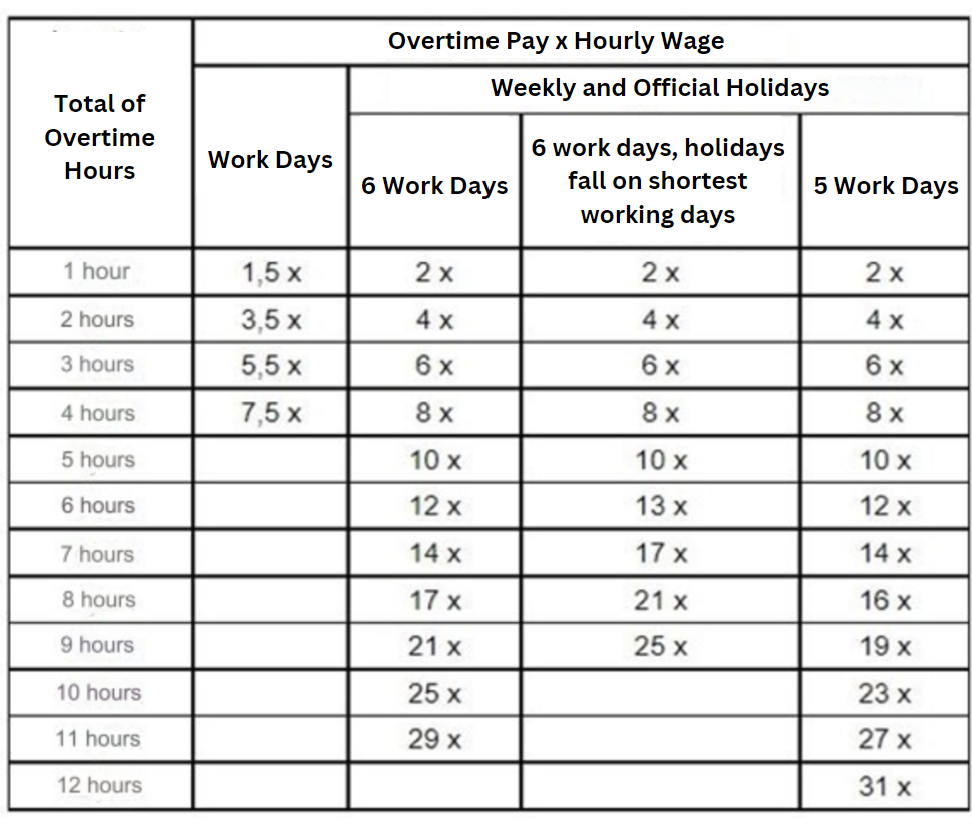
Indonesia’s labor laws are designed to protect workers while facilitating efficient business operations. Overtime work is regulated with specific calculations to ensure fair compensation, where overtime wages are based on an employee’s base salary divided by 173 hours for a standard work month. This clarity helps maintain worker satisfaction and productivity, providing stability for businesses.
In Batam, industries like electronics manufacturing and logistics often operate on a three-shift system to maximize productivity, typically consisting of three 8-hour shifts for 24/7 operations. Some companies may also use a two-shift system with 12-hour shifts over a 6-day workweek. To support night shift workers, businesses often provide incentives like snacks and drinks to help maintain their energy levels.
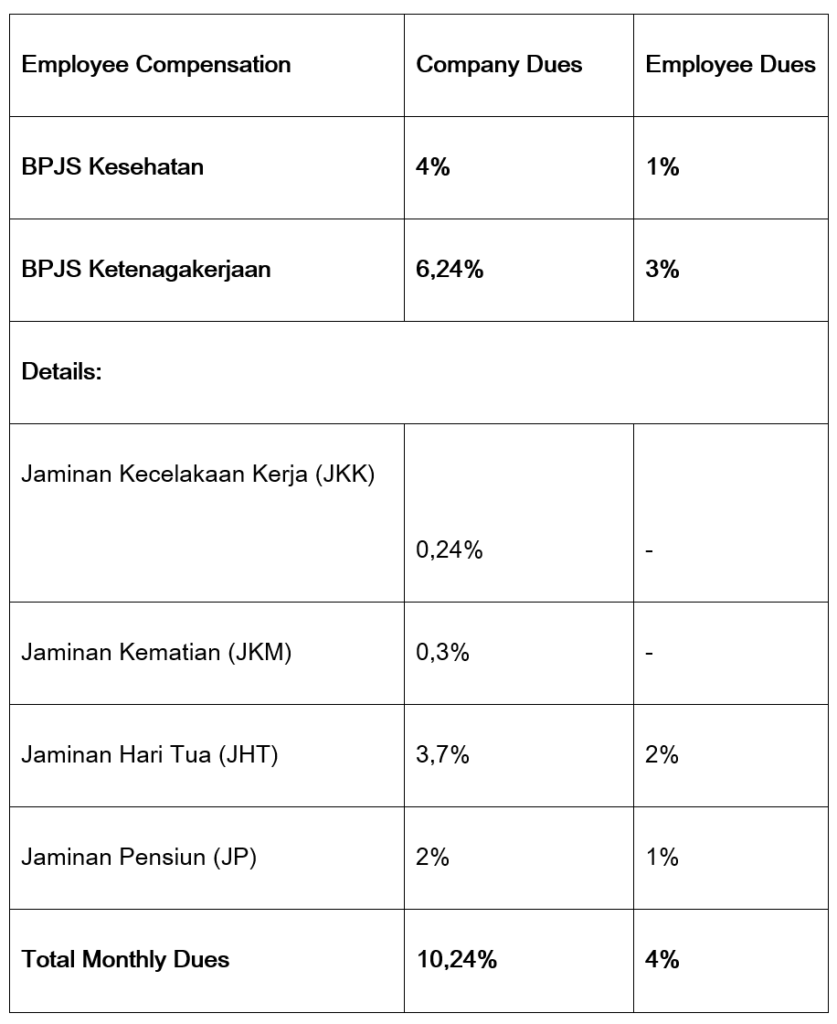
A crucial aspect of Batam’s labor environment is the comprehensive social security system managed by BPJS, which includes BPJS Kesehatan for health insurance and BPJS Ketenagakerjaan for employment protection. This system ensures workers have access to healthcare and support in case of workplace accidents, contributing to workforce stability.
Recruitment Trends and Talent Availability
Batam’s labor market is dynamic, with diverse recruitment channels for both blue-collar and white-collar job roles. For blue-collar positions, companies primarily utilize local job portals, social media, and HR outreach to attract skilled workers, reflecting the high demand in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and assembly. In contrast, white-collar recruitment, especially for managerial roles, often involves professional platforms like LinkedIn and headhunters, ensuring access to top-tier talent. For critical positions, companies may even recruit expatriates from their head offices to bring in specialized expertise.


A unique aspect of Batam’s workforce is its multilingual capabilities, particularly in Mandarin. Many locals possess basic Mandarin skills, which is advantageous for businesses engaged in trade with Mandarin-speaking markets, such as China. The presence of a sizable Chinese community and Mandarin language programs in schools enhance this linguistic skill among the population. This capability not only fosters smooth international business relationships but also positions Batam as a multicultural city ready to connect local workers with the global job market.

